Pages
Build and/or verify cooling tower performance and efficiency with TURBOsplash PAC ®™ and NERI Calculator
Labels
Comments on cooling tower
(1)
Cooling Tower Calculations
(28)
Cooling Towers
(18)
Cross-flow and Counter-flow
(25)
Energy
(37)
Environment
(35)
Evaporative Cooling Towers
(42)
Geothermal Energy
(5)
Heat Transfer
(15)
How to Design the Water Cooling Towers
(34)
How to Design Water Cooling Towers
(25)
NERI Calculator
(15)
Optimizing
(7)
Software cooling tower
(6)
TURBOsplash PAC ®™
(24)
Water
(27)
Water Cooling Tower
(28)
Water Cooling Towers
(4)
What happens inside TURBOsplash PAC
(6)
what happens inside TURBOsplashPAC ® TM
(7)
Why install TURBOsplash PAC ®™
(4)
Why install TURBOsplashPAC ® TM
(11)
Showing posts with label Cross-flow and Counter-flow. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Cross-flow and Counter-flow. Show all posts
November 11, 2019
September 9, 2019
TURBOsplash PAC ®™ - What is it?
TURBOsplash PAC ®™ is a filling material for systems that exploit the physical principle of "mass transfer" to migrate from one element to another.
TURBOsplash PAC ®™ is employed in water cooling towers, where the two elements are water and air. This material is used by prestigious companies that build cooling towers or replace/retrofit traditional material (film and grids). As a result, the increased performance is sensitive and allows for a long functioning period. TURBOsplash PAC ®™ was invented by Bruno Neri and now commercialised by TSI company and other partners under authorized license. It is patented in most industrialized countries, where it is installed and in use with satisfied customers for over 25 years.
September 2, 2019
August 19, 2019
August 12, 2019
Feedback from our followers
A follower commented: "I had no idea what cooling towers were used for. "
Today's cooling towers have come a long way from the old and inefficient simple heat exchanger of their ancestors.
 |
| An old cooling tower |
This aim of this blog is to continue contributing to improving cooling tower efficiency and performance, by understanding and resolving problems that could result from bad tower design and/or management.
August 5, 2019
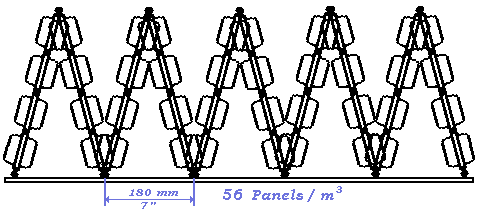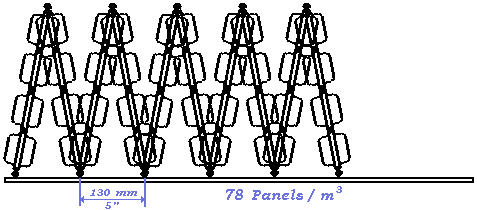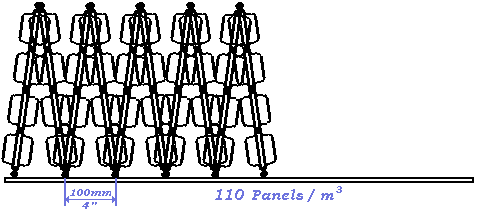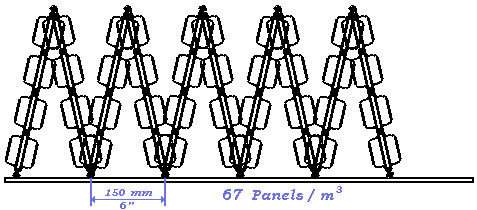
Evaporative Panels for all WATER COOLING TOWERS - Modular Polypropylene Injection Molded
TURBOsplash PAC ®™ is a bottom supported modular evaporation panel system for making cooling tower fill modules.
TURBOsplash PAC ®™ panels are injection molded in polypropylene, constructed with a 300mm (@1 foot) by 600mm (@2 feet) U-channel framework and with a total of 38 blades molded perpendicular to this framework.
The panels are manufactured with molded-on spacer straps, which are used in conjunction with pins molded on the panel ends to stabilize different triangular structures in any of six density/widths.
Concerning Wet Bulb Temperature
What is Wet bulb ? Cooling tower cools water by evaporating some of the water, and water cannot evaporate once air is 100% saturated. At wet bulb temperature air is 100% saturated, therefore water cannot be cooled below wet bulb temperature.
July 29, 2019
TURBOsplash PAC ®™ - A versatile fill material for a cost-effective solution
The following pictures show the versatility of TURBOsplash PAC ®™ fill material for evaporative cooling towers; that is, the same panel offers various possibilities to create different configurations with minimum warehouse immobilization.
 |
| 2 layer |
 |
| Example of 5 different configurations |
 |
| Panel configuration |
 |
| Panels come with joining strips |
 |
| Loading container |
 |
| Ready for loading |
 |
| Ready for air shipment |
July 22, 2019
Installation of TURBOsplash PAC ®™ in Field Erected FRP Cooling Tower
The picture shows the work in progress of installing TURBOsplash PAC ®™ fill material in field erected cooling tower made of FRP (Fiber Reinforced Polymer).
July 15, 2019
TURBOsplash PAC ®™ installation progress
The following pictures illustrate the work progress of TURBOsplash PAC ®™ fill material to be installed in erected counter-flow cooling towers.
July 8, 2019
Retrofitting with TURBOsplash PAC ®™ to increase efficiency
These pictures illustrate a few aspects of a recent job carried out with success and much satisfaction. The job entailed substituting old film with TURBOsplash PAC ®™ installed in different layers, and with different configurations to improve the efficiency of the cooling tower.
 |
| TURBOsplash PAC installed each layer of different configuration |
 |
| TURBOsplash PAC ready to install |
June 10, 2019
TURBOsplash PAC ®™ fill material panels
Images of TURBOsplash PAC ®™ fill material panels, packaged and prepared for shipment/install in cooling towers.
March 25, 2019
The importance of water in the cooling tower industry - Water (part 9)
HOW TO MEASURE THE EFFICIENCY OF A COOLING TOWER
In the design process of a cooling tower, there is a need to have at least seven data values or rather 7 variables. If only one of these values is changed, the result will be a cooling tower with different dimensions.
Some of this data or design values are questionable, such as the temperature of the air at wet-bulb temperature, that seems to shift every year for speculation reasons.
To measure the efficiency of each tower, there is a need to know the exact design data and the theory that allows designing the tower, hence, knowing the values detected by lab effective testing.
All this will be treated in another chapter with interesting considerations.
Now we shall discuss how to evaluate the efficiency of the cooling tower in a simple and practical way.
We shall use the method that will allow, at least, to compare the efficiency of the tower at the any given time with the efficiency of the tower at the time it was installed: in other words, the degradation of efficiency (if it exists).
The main element for cooling water is air. The amount of air is essential for the amount of heat to dissipate, temperature, etc.
The amount of air measurement is synonymous of tower efficiency.
The degradation over time can decrease the amount of air in the tower because there are occlusions within the filling material that block the passage of air. Occlusions may originate from collapsed material, limestone, dust, algae, etc.
The water will always circulate.
The masses of water and air inside the tower are huge. The water weight is about 15,000 to 30,000 kg/m2 of the tower. Thus, the water will always fall via preferential routes: holes or by laminating on the tower walls. The amount of air passing through the tower is of vital importance.
A quick way to know the efficiency of the cooling tower is to measure the amount of air all you need to is to measure the speed of the air incoming to the tower or outgoing from the tower.
The speed in m/s and is measured with an anemometer (a very simple tool with fan). This tool is used to measure wind speed, etc. Hence, the speed through the cross-section (m2 top view) of the tower MUST be between 2.5 m/s and 4 m/s.
If the speed is lower than 2.5 m/s, the amount of air through the tower is very low and the cooling is compromised. The tower will be not efficient!
This method is basically a rule of thumb, but it serves as an alarm that a more accurate review is required.
October 18, 2016
The importance of water in the cooling tower industry - Water (part 10)
WHAT ARE THE CONSEQUENCES OF A COOLING TOWER OPERATING AT LOW EFFICIENCY?
 |
| Cooling tower detailed calculations |
A low efficient cooling tower brings very serious consequences.
| Bruno Neri |
The tower is part of a system designed to dispose residual waste heat from the production plant or other primary system. The lower efficiency of the tower affects the performance of the primary plant with considerable waste of energy and, most of all, reduction or lack of production.
CONSTRUCTION OF A COOLING TOWER: TIPS ON ITS COMPONENTS AND THEIR USE.
As we saw, the cooling tower is an essential part of the plant system and, generally, it is separated from the primary plant system to which it drives.
The cooling tower is normally ignored until it goes into failure. Hence, the choice of components is of utmost importance.
Choose a tower made of stainless steel. Towers that need to be installed in heavy environments, such as chemical industries, choose polyester reinforced with glass fiber.
CONSTRUCTION OF A COOLING TOWER: TIPS ON ITS COMPONENTS AND THEIR USE.
As we saw, the cooling tower is an essential part of the plant system and, generally, it is separated from the primary plant system to which it drives.
The cooling tower is normally ignored until it goes into failure. Hence, the choice of components is of utmost importance.
Choose a tower made of stainless steel. Towers that need to be installed in heavy environments, such as chemical industries, choose polyester reinforced with glass fiber.
We have witnessed towers that have been operating for over 30 years, in these heavy environments, in perfectly stable structure.
Other useful tips and / or necessary will be exposed our next documentation work for publishing:
"A practical guide for the design of components that impact cooling tower thermal efficiency"
October 10, 2016
The importance of water in the cooling tower industry - Water (part 9)
HOW TO MEASURE THE EFFICIENCY OF A COOLING TOWER
In the design process of a cooling tower there is a need to have at least seven data values, or rather 7 variables. If only one of these values is changed, the result will be a cooling tower with different dimensions.
Some of this data or design values are questionable, such as the temperature of air at wet-bulb temperature, that seems to shift every year for speculation reasons.
To measure the efficiency of each tower, hence, there is a need to know the exact design data and the theory that allows to design the tower, knowing the values detected by lab effective testing.
All this will be treated in another chapter with interesting considerations.
Some of this data or design values are questionable, such as the temperature of air at wet-bulb temperature, that seems to shift every year for speculation reasons.
To measure the efficiency of each tower, hence, there is a need to know the exact design data and the theory that allows to design the tower, knowing the values detected by lab effective testing.
All this will be treated in another chapter with interesting considerations.
Now we will discuss how to evaluate the efficiency of the cooling tower in a simple and practical way.
We shall use the method that will allow, at least, to compare the efficiency of the tower at the any given time with the efficiency of the tower at the time it was installed: in other words, the degradation of efficiency (if it exists).
The main element for cooling water is air. The amount of air is essential for the amount of heat to dissipate, temperature, etc.
The amount of air measurement is synonymous of tower efficiency.
The degradation over time can decrease the amount of air in the tower because there are occlusions within the filling material that block the passage of air. Occlusions may originate from collapsed material, limestone, dust, algae, etc.
We shall use the method that will allow, at least, to compare the efficiency of the tower at the any given time with the efficiency of the tower at the time it was installed: in other words, the degradation of efficiency (if it exists).
The main element for cooling water is air. The amount of air is essential for the amount of heat to dissipate, temperature, etc.
The amount of air measurement is synonymous of tower efficiency.
The degradation over time can decrease the amount of air in the tower because there are occlusions within the filling material that block the passage of air. Occlusions may originate from collapsed material, limestone, dust, algae, etc.
The air will always circulate.
The masses of water and air inside the tower are huge. The water weight is about 15,000 to 30,000 kg/m2 of the tower. Thus, the water will always fall via preferential routes: holes or by laminating on the tower walls. The amount of air passing through the tower is of vital importance.
A quick way to know the efficiency of the cooling tower is to measure the amount of air all you need to is to measure the speed of the air incoming to the tower or outgoing from the tower.
The speed in m/s and is measured with an anemometer (a very simple tool with fan). This tool is used to measure the wind speed, etc. Hence, the speed through the cross section (m2 top view) of the tower MUST be between 2.5 and 4 m/s.
If the speed is lower than 2.5 m/s, the amount of air through the tower is very low and the cooling is compromised. The tower will be not efficient!
This method is basically a rule of thumb, but it serves as an alarm that a more accurate review is required.
October 1, 2016
The importance of water in the cooling tower industry - Water (part 8)
COOLING TOWER

Cooling tower design require water and air related data.
Data concerning the water include flow rate, water temperature going into the tower, and temperature going out of the tower. This data is provided by the cooling tower plant design.
Data concerning the air is provided by weather statistics site where the tower is located or where it will be installed, and is given in percentage hours per year or summer dry bulb temperature and relative humidity, measured at the same instant of detection of the dry bulb temperature.
The amount of air required in the tower is given by the design results, and the size of the cooling tower depends directly on this data.
Hence, one must determine the air velocity inside the tower, the power of the fan motors, and all the characteristics of the tower sized based on the efficiency of individual components, including the main component which is the fill material that allows heat exchange of water / air.
Cooling tower design require water and air related data.
Data concerning the water include flow rate, water temperature going into the tower, and temperature going out of the tower. This data is provided by the cooling tower plant design.
Data concerning the air is provided by weather statistics site where the tower is located or where it will be installed, and is given in percentage hours per year or summer dry bulb temperature and relative humidity, measured at the same instant of detection of the dry bulb temperature.
The amount of air required in the tower is given by the design results, and the size of the cooling tower depends directly on this data.
Hence, one must determine the air velocity inside the tower, the power of the fan motors, and all the characteristics of the tower sized based on the efficiency of individual components, including the main component which is the fill material that allows heat exchange of water / air.
September 26, 2016
The importance of water in the cooling tower industry - Water (part 7)
Process plants that can be cooled with evaporation systems.
The importance of disposing quantity of energy.
Efficiency of the cooling system.
The importance of disposing quantity of energy.
Efficiency of the cooling system.
| Image from previous post "NERI Calculator". Click on the above image to learn more about the calculator. |
From what has been written on this subject, the disposal of heat from evaporative cooling towers use something in particular, that is, disposing large amounts of heat from the water by means of the air: two natural elements.
Heat disposal has, therefore, a relatively low cost.
To name a few examples where towers are used:
(a) disposing heat from the various refrigeration groups and city building air conditioning condensers.
(b) in industries such as oil refineries, chemical plants,
(c) in industrial process plants for the production of food products,
(d) in thermoelectric power plants,
(e) in geothermal systems.
(f) …
Obviously each type of installation has different requirements for heat disposal (amount of cooled water). Temperatures and their range must be designed appropriately and carefully, and, most of all, the air thermal characteristic data to be considered for cooling tower design.
Air data has to include temperature, humidity and altitude related to the location of the tower. These three values (temperature, humidity, altitude) are very important.
If the data is not chosen correctly, this can lead to the wrong tower sizing, up to three or four times higher, or lower, than the actual needs of the system.
If the tower sizing is higher than the correct value, this will lead to waste of material and, hence, higher cost of the system. On the other hand, if faulty sizing will lead to equipment that is not adequate to the system, hence, useless!
September 19, 2016
NERI Calculator
When it comes to evaporative water cooling towers, whether you're are part of the design team or maintenance operations, NERI Calculator helps ensure that the functionality of the tower is optimal and efficient, hence, maintaining plant's productivity at maximum level.
Design
Design
For maximum efficiency, in the design phase of the evaporative cooling tower project, NERI Calculator returns the optimal size of the tower needed to serve a predesigned plant system.
Maintenance
In normal maintenance operations, NERI Calculator verifies tower performance based on the actual tower data.
What are the risks of a poor functioning tower?
- Tower driven system will not function correctly
- Loss of productivity of the plant
- Could cause heavy damage
- Impact on the Environment
The cost of running a bad designed cooling tower could be high!
NERI Calculator covers two type of evaporative water cooling towers:
- Counter-flow: a water cooling tower design where the air-flow is directly opposite of the water-flow.
- Cross-flow: a water cooling tower system design in which the air-flow is directed perpendicular to the water-flow. Air flow enters one or more vertical faces of the cooling tower to meet the fill material.
If your tower is counter-flow, then try our NERI Calculator tool for free. When you sign up, we offer you a 1-day free trial of 50 calculations.
If your tower is cross-flow, then contact us and we'll do the calculations for you.
NERI Calculator is not only used for design purposes, but it's a tool to use always during on-going activities for monitoring and controlling cooling tower performance.
“Prevention is better than cure”
“Prevention is better than cure”
NERI Calculator will prevent damages resulting from a poorly functioning cooling tower, by verifying that the data is correct and/or has not been modified. Poor functioning cooling towers will have bad consequences not only on the cooling tower, but mostly on any production system served by the tower. All this damage and loss can be translated in huge economic loss!
How to use NERI Calculator:
STEP 1
| Diagram 1 |
STEP 2
| Diagram 2 |
STEP 3 AND 4
| Diagram 3 |
STEP 5 AND 6
| Diagram 4 |
FINAL DATA
| Diagram 5 |
PRICE
| Diagram 6 |
April 4, 2016
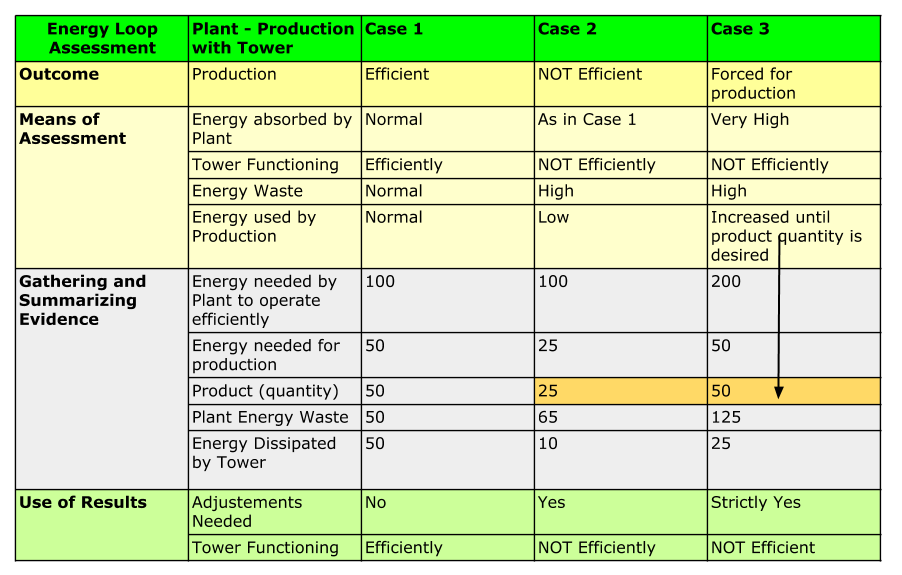
Energy Loop Assessment for Water Cooling Tower
The purpose of this post is to stimulate you to share your experiences and thoughts on energy related issues.
The following table and related diagrams illustrate how to assess energy in a production plant scenario served by a water cooling tower. It includes three different cases with different criteria and different situations. The numbers shown are strictly EMBLEMATIC for the only purpose of illustrating the cases.
Case 1: Plant - Production with Tower; Outcome : EFFICIENT
 |
| Diagram for Case 1 |
Case 2: Plant - Production with Tower: Outcome : NOT EFFICIENT
 |
| Diagram for Case 2 |
Case 3: Plant - Production with Tower; Outcome: FORCED FOR PRODUCTION
 |
| Diagram for Case 3 |
May 16, 2015
The importance of water in the cooling tower industry - Water (part 10)
WHAT ARE THE CONSEQUENCES OF A COOLING TOWER OPERATING AT LOW EFFICIENCY?
 |
| Cooling tower detailed calculations |
A low efficient cooling tower brings very serious consequences.
| Bruno Neri |
The tower is part of a system designed to dispose residual waste heat from the production plant or other primary system. The lower efficiency of the tower affects the performance of the primary plant with considerable waste of energy and, most of all, reduction or lack of production.
CONSTRUCTION OF A COOLING TOWER: TIPS ON ITS COMPONENTS AND THEIR USE.
As we saw, the cooling tower is an essential part of the plant system and, generally, it is separated from the primary plant system to which it drives.
The cooling tower is normally ignored until it goes into failure. Hence, the choice of components is of utmost importance.
Choose a tower made of stainless steel. Towers that need to be installed in heavy environments, such as chemical industries, choose polyester reinforced with glass fiber.
CONSTRUCTION OF A COOLING TOWER: TIPS ON ITS COMPONENTS AND THEIR USE.
As we saw, the cooling tower is an essential part of the plant system and, generally, it is separated from the primary plant system to which it drives.
The cooling tower is normally ignored until it goes into failure. Hence, the choice of components is of utmost importance.
Choose a tower made of stainless steel. Towers that need to be installed in heavy environments, such as chemical industries, choose polyester reinforced with glass fiber.
We have witnessed towers that have been operating for over 30 years, in these heavy environments, in perfectly stable structure.
Other useful tips and / or necessary will be exposed our next documentation work for publishing:
"A practical guide for the design of components that impact cooling tower thermal efficiency"
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)